It’s time to talk about it. What’s algorithmic trading?
I’ve been asked many questions related to algorithmic trading; here are some:
- Are there any advantages to trading with automated strategies? Why use algo trading?
- How can institutional and professional traders execute trades at super speed or make decisions based on complex mathematical models? Can I do the same? How? Is it expensive?
- How to code algo trading?
- How does algo trading software work?
- Is algorithmic trading free?
- Which algorithmic trading is best?
I am sure that you have many more.
In this comprehensive guide, I will explain in plain English the concept of algorithmic trading, its benefits, how it works, and a few practical tips to get you started. I will be leaving some trading strategies as examples for you to download at the end. Promise.
So, sit back, relax, open your mind and get ready to be transported to another dimension where we let the machine make decisions for us based on how we have trained them.
Let’s dive in!
Takeaways
Algorithmic Trading Definition: Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading, automated trading, or systematic trading, is a method where trades are executed using pre-programmed instructions based on predefined rules and criteria. These instructions are typically written in specific programming languages like TradeStation EasyLanguage, MultiCharts PowerLanguage, Pinescript or Python, to mention just a few.
Advantages of Algorithmic Trading: The benefits of algorithmic trading include speed and efficiency, as computers can analyse and execute trades faster than humans. It also reduces emotional biases, allows for backtesting and optimization of strategies using historical data, offers diversification and risk management, and can lead to reduced transaction costs.
Risks in Algorithmic Trading: Despite its advantages, algorithmic trading comes with challenges, including market volatility and liquidity issues, which can lead to rapid price fluctuations and slippage. System failures and technology risks, such as technical glitches or software bugs, can also disrupt trading operations.
Common Algorithmic Trading Strategies: Some prevalent algorithmic trading strategies include:
+ Trend Following: Aims to capture profits by identifying and riding market trends.
+ Mean Reversion: Based on the idea that prices tend to revert to their average over time.
+ Arbitrage: Exploits price discrepancies across different markets or exchanges.
Tools and Resources: Success in algorithmic trading requires the right tools and resources. Essential elements include algorithmic trading software like TradeStation and MultiCharts, data providers and APIs for accessing real-time and historical market data, and continuous learning and adaptation to stay updated with market dynamics and technological advancements.
Algorithmic Trading: Understanding the Basics
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading, automated trading, mechanical trading or systematic trading, is a method of executing trades using pre-programmed instructions usually written with a specific programming language code.
For example, TradeStation EasyLanguage is a proprietary programming language created by TradeStation Security for its workstation platform.
These instructions are based on a set of predefined rules and criteria, which traders like you use to define trading strategies.
Now, let’s explore the fundamental aspects of algorithmic trading and its advantages.
Understanding the Basics
Simplifying the definition of how algorithmic trading works, let’s say that it involves using a computer program that executes trades on the basis of a set of rules predefined on your behalf automatically.

These programs can utilize simple logic or more complex mathematical models, statistical analysis, historical data, time, etc., to execute trade orders in near real-time (if you don’t consider aspects like distance from the exchange where the trade is routed, for example).
The goal is to be more efficient in our trading activities and profit from market inefficiencies within a fraction of a second if you consider models like HFT (High-Frequency Trading). Something that only big institutional organisations with deep pockets have the luxury to benefit from. I am sure you’ve heard of HFT in the news or on the internet here and there.
For humans like me, the goal is to run a portfolio (multiple) of strategies automatically while I work on my 9to5 job.
The real edge (advantage) here is to increase your trading efficiency and take advantage of entering and exiting trades when the opportunity manifests itself. For example, while you sleep.
Manual intervention is minimized with algorithmic trading, and trades are executed automatically based on predetermined conditions. This has another advantage of reducing emotional biases often associated with humans, such as fear, greed or intuition and allowing for faster and more precise trade execution.
Advantages of Algorithmic Trading
Speed and Efficiency: One of the critical benefits of algorithmic trading is its speed.
Computers can analyze market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute trades faster than humans. It enables algorithmic traders to exploit more trading opportunities than manual traders can and leverage probability for a better monetary return.
Reduction of Emotional Biases: Emotions can significantly impact trading decisions.
By utilizing algorithms, traders can reduce human emotions in the trading process. This helps maintain a disciplined approach and stick to the predefined trading strategy without being influenced by market volatility or other external factors. Maintaining emotions under control needs some work, even in the world of automatic trading. The software assists us in dealing with dealing with emotional biases and does not eliminate the problem.
Backtesting and Optimization: Algorithmic trading systems allow traders to backtest their strategies using historical data.
This allows traders to test a trading strategy before risking real money and trading capital. Traders can also fine-tune their algorithms and optimize them based on the backtesting results to improve performance.
Important note on “backtesting results to improve performance”:
past performances are not indicative of future returns.
Diversification and Risk Management: Algorithmic trading enables us to diversify our trading portfolios across multiple instruments and markets.
By simultaneously trading in different assets, traders can spread the risk and reduce exposure to any single trade or market. Additionally, algorithms can be designed to incorporate risk management techniques – my favourite – such as stop-loss orders to limit potential losses or scaling in and scaling out methods to enter “gently” on certain trades before expanding your position only if possible.
Reduced Transaction Costs: Algorithmic trading can help minimize transaction costs by executing trades at optimal prices and volumes, potentially resulting in improved execution prices and reduced slippage.
The algorithms have the ability to “follow” the price more efficiently than a manual click for a trade execution. This is even more noticeable on lower trading timeframes, with charts on a minute bar, for example.
Keeping transition costs low is important for having overall healthy returns within your trading account.
Algorithmic trading is a powerful tool that leverages technology and data analysis to automate trading activities. By understanding the basics and learning how to take advantage of its benefits, traders like you can potentially enhance their trading strategies and improve their overall performance.
Getting Started with Algorithmic Trading
I want to explore and share what are the fundamental steps to get started with algorithmic trading.
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading or automated trading, refers to using computer programs to execute trading strategies.
What are the key components of getting started with algorithmic trading?
Choosing a Trading Platform
The first step in algorithmic trading is choosing a reliable platform with a trading strategy development environment.
This platform serves as the interface between you and the market. It should provide the necessary tools and features to test and execute your trading strategies effectively.
When selecting a trading platform, consider factors such as user-friendly programming language, robustness, availability of technical indicators, strategies and code examples and, most important of all, consider the compatibility and support that the platform has with the main brokers used by retail traders like us.
Below are some popular trading platforms that offer a wide range of features and are suitable for beginners, listed in order of friendliness [in my opinion]
- TradeStation Securities – https://www.tradestation.com/platforms-and-tools/desktop/
- MultiCharts – https://www.multicharts.com/features/
- Trading View – https://www.tradingview.com/features/
I use the first two for my trading as I can code my strategies using EasyLanguage as the programming language and run on both platforms, allowing me to access more financial markets as I would be able to by choosing only one.
Setting Up a Trading Account
Once you’ve chosen your trading platform, setting up a trading account is next.
This involves creating an account with a brokerage firm that is compatible with your chosen trading platform. A brokerage firm acts as an intermediary between you and the market, executing trades on your behalf.
During the account setup process, you will typically need to provide personal information and financial details.
Choosing a reputable brokerage firm is a must, as it can reduce the risk of potential problems with brokerage firms going bust with our money, as happened with MF Global.
In the evaluation, offering competitive commission rates, reliable customer support, and a wide variety of financial instruments to trade are also important.
Building Your Trading Strategy
Now that you have a trading platform and a trading account (it is essential to have access to a paper trading account), it’s time to get crafting and start building our automatic strategies.
As said above, a trading strategy is a predefined set of rules determining when and how to enter or exit trades.
Where do I start? What would be the first thing I can do to get going?
Assuming that we have the necessary knowledge…
First, we should identify what edge (advantage) a trading instrument has and then choose a trading strategy that looks to take advantage of that edge. There are numerous trading strategies available, ranging from simple to complex.
As an example, let’s take the Forex pair GBP/USD.
Can we identify something that statistically repeats itself and take advantage of it, writing a trading system that follows those rules?
Yes, we can. And it’s not bad at all. This kind of edge is categorised as a BIAS in statistics. We’ll explore the strategy in the next section.
Alongside bias strategies, other common trading strategies include trend following, mean reversion, breakouts, and momentum trading.
When you are starting out, I’d advise you to adopt a “follow and learn” approach to get some experience in creating a strategy, testing it and running it live with real money.
Immediately, you will discover if you have a good feeling about the chosen strategy or if the strategy risk profile is right for you. An all-rainbow of emotions will surface as soon as you release your right-click button on your mouse to enable automatic trading on the platform.
At tradewithcode, we go deep into understanding and learning more about the different trading strategies with code examples and backtesting results – a benefit of joining the tradewithcode community.
After these initial steps of getting started with algorithmic trading, I hope you are ready to delve even deeper into algorithmic trading and explore more advanced topics such as backtesting, risk management, and optimization of trading parameters.
The Components of Algorithmic Trading
In algorithmic trading, three key components form the foundation of the trading process.
These components are essential for successful implementation and execution. Let’s explore each component in detail:
Data Analysis and Research
Data analysis and research play a crucial role in algorithmic trading. Traders must gather and analyze vast amounts of financial data to identify profitable trading opportunities. This involves studying historical price trends, market indicators, and economic data to make informed trading decisions.
This data-driven approach helps develop effective trading strategies that capitalise on market inefficiencies and generate profits.
Let’s continue with our GBPUSD example and find if any biases can be interesting to analyse.
Here at tradewithcode, we use a tool called data analyser to analyse huge quantities of data in a matter of minutes, giving us a sort of superpower.
If you are into Microsoft Excel and you know how to use it for data analysis, you can do those tests using Excel; it will take longer, but it is possible. A tool like Data Analyser speeds everything up and keeps things focused on what we need.
Below is the GBPUSD prices dataset analysis from the beginning of 2002 until mid-2013.
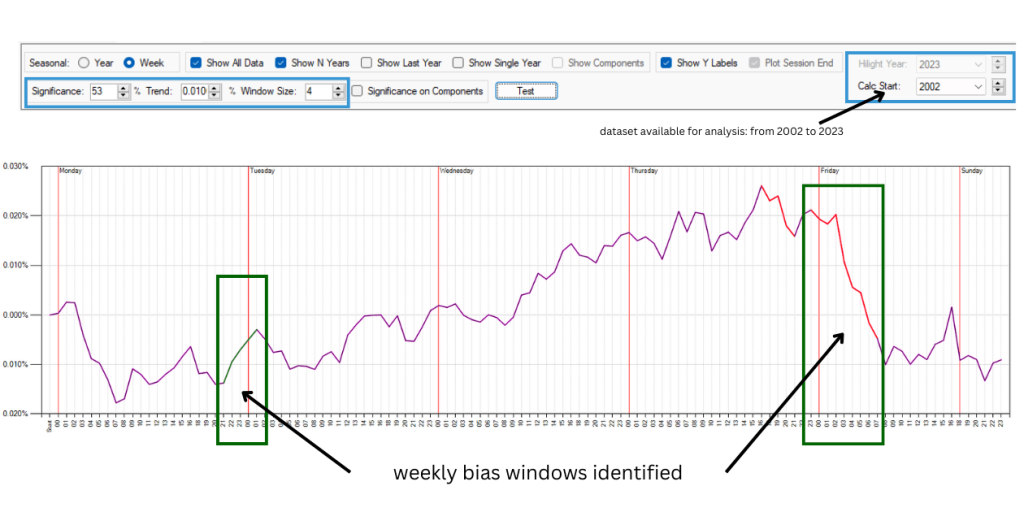
As we can see, there are two interesting bias windows between 2002 and 2013, where on a Monday and on a Thursday, for the 53% of the time, the price went up, and the price went down at a specific time of the day during the week.
It’s not as good as seeing the future, but we have a great advantage if we consider these terms.
Let’s validate if we can build a trading system with that information.
Building and Testing Trading Models
Once the necessary data has been collected, traders build and test trading models. These models serve as the backbone of algorithmic trading strategies.
EasyLanguage will be used to codify the trading model identified. Many other programming languages, such as Python or R, can be used to develop mathematical algorithms that execute trades based on predefined rules. I’m unsure for beginners if these are the right way forward.
I’ll stick with EasyLanguage for now as it’s more user-friendly and allows us to focus on other important aspects without being too worried about learning a complex programming language.
Before writing any code, I want to validate if what I have seen on the tool is sound! And it looks like it.
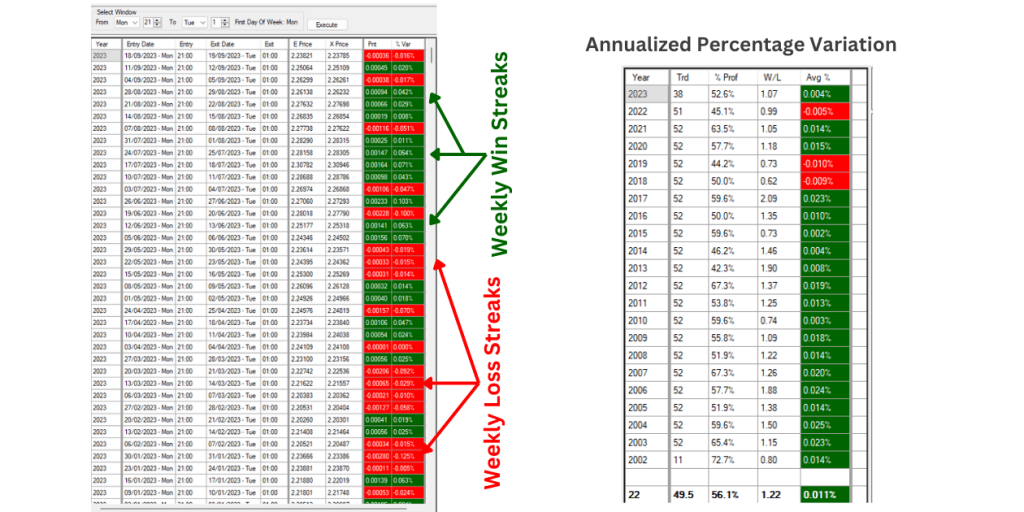
Our bias strategy has a win/loss ratio of 1.22 – this ratio indicates how many times a strategy will perform successful, money-making trades relative to how many times it will have money-losing trades.
During the testing phase, evaluating a trading strategy performance using historical data is a process known as backtesting. It helps assess the strategies’ profitability and robustness and allows us traders to refine and optimize trading models to maximize returns and minimize risks.
The backtesting of our GBPUSD Bias has a backtesting analysis with an uptrend result of the last 22 years, which means that the strategy in that period has made money.
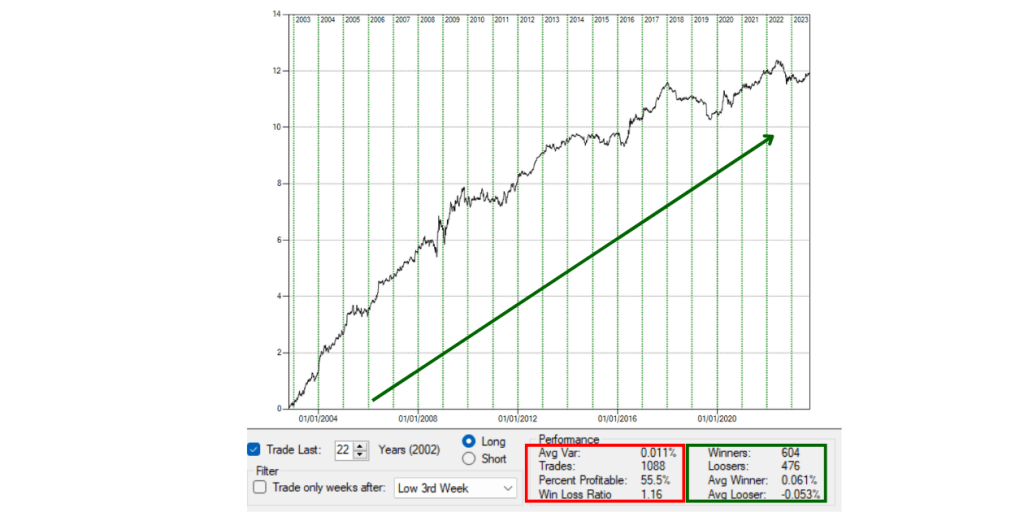
I very much like the results of this analysis, and now let’s code it and test it on a chart within the platform.
I used TradeStation for it.
The BIAS identified is defined in plain English as
Buy Monday @ 21:00, Sell Tuesday @ 01:00.
That’s it!
So if we bought 1 lot of GBPUSD currency pair every Monday at 9 pm EST and we had sold it back on Tuesday at 1 am EST every week for the last 20 and plus years, we could have seen the performance in the graph above for our strategy.
TIP: Be careful with the time zones as they change everything.
Here is the code in EasyLanguage:
//Buy Monday @ 21:00, Sell Tuesday @ 01:00
if dayofweek(date) = monday and time = 2000 then
buy nCon contract next bar at open;
if mp = 1 and dayofweek(date) = tuesday and time = 0000 then
sell nCon contract next bar at open;Below is the equity curve result of the full strategy, combining both biases identified for the trading week of GBPUSD.
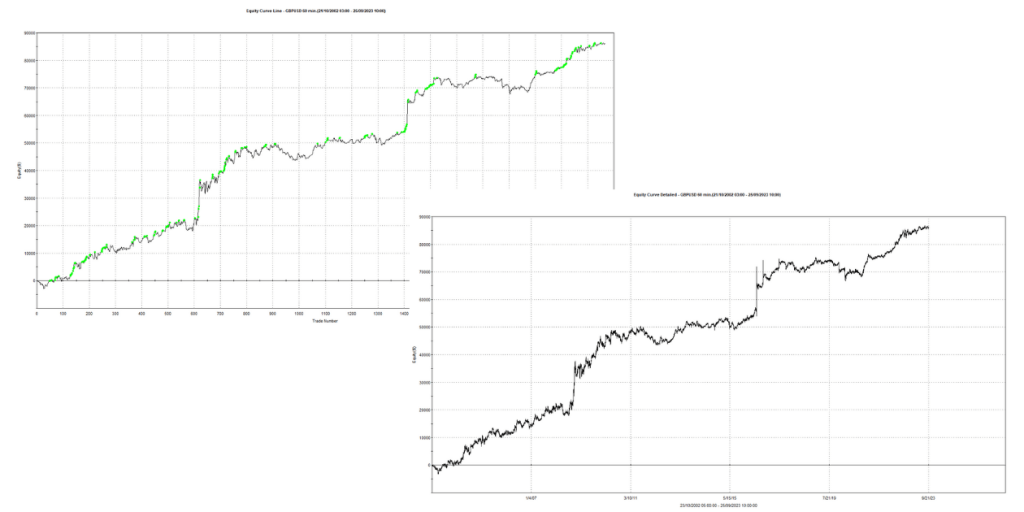
The result shows a good potential for an interesting strategy in this category. More validation work is needed before putting it live with real money, but it’s a positive outcome.
If you’re interested in learning more about building and testing trading models, you can refer to our weekly workshop agendas, part of our premium membership, for comprehensive strategy development and techniques.
Execution and Monitoring
The final component of algorithmic trading is the execution and monitoring of trades.
Once the trading models are developed, tested and validated, we can deploy them to our “live” environments to automatically execute trades based on predefined rulesets and parameters.
This eliminates the need for manual intervention and ensures timely execution in fast-paced markets. Or, as in our case, at 1 a.m. at night if you live in New York (USA).
Automation doesn’t mean run and forget – the contrary. We, as traders, also need to monitor our trading algorithms to ensure they perform as expected in every situation and be timely in addressing potential machine issues due to the million factors we have no control over.
This continuous monitoring helps in adapting to changing market conditions and maximizing profitability.
By understanding and effectively utilizing these components of algorithmic trading – data analysis and research, building, testing and validation of trading models, and closing the loop with execution and monitoring – we have the opportunity to enhance our trading strategies and potentially achieve consistent profitability in the financial markets.
Risks and Challenges in Algorithmic Trading
Market Volatility and Liquidity
With trading and also with algorithmic trading, one of the major risks that traders face is market volatility and liquidity. This refers to the rapid and unpredictable changes in market prices and the ability to execute trades quickly and, more importantly, at desired prices.
During periods of high market volatility, such as economic crises or major news events, prices can fluctuate significantly within seconds. This can lead to slippage (the real enemy here), where trades are executed at prices different from the intended ones.
It is crucial for mechanical traders to have robust risk management systems in place to mitigate and handle potential losses properly during volatile market conditions.
I believe that risk management is probably the first element that every beginner should learn when they get into trading. I made the mistake of not caring too much about it, and I paid for it.
Today, it is a different story; my trading systems are set not to enter trades if volatility is too high for my trading account to handle if anything goes wrong.
That keeps me and my trading account on the safer side from extinction from trading.
Liquidity is another important factor to consider. It refers to the ease with which traders can buy or sell securities without causing substantial price movements. In illiquid markets, it can be challenging to execute trades as you won’t have anyone on the other side of the trade to buy at the price you want to sell, which may significantly impact the take-home profitability.
A very important aspect that we must carefully analyse when we decide to trade a financial instrument is its market liquidity and adjust our algorithms accordingly to avoid any negative effects on our trading strategies… or, more sensibly, don’t trade that market if the effects of slippage reduce the risk-reward ratio to a point that is not worth it the risk anymore.
We want to get in and get out easily from a trade and quickly transform the gains into cash so we can efficiently re-utilise it on new market opportunities.
System Failures and Technology Risks
Algorithmic trading heavily relies on sophisticated systems and advanced technologies. However, with all these techs involved come potential risks and challenges.
System failures can occur due to technical glitches, software bugs, or hardware malfunctions. These failures can disrupt trading operations and lead to financial losses. It is essential for algorithmic traders to have robust backup systems and disaster recovery plans to minimize the impact of system failures.
As crazy as it may seem to think in this way, it can be what can make the difference between surviving and getting your trading account wiped out because you couldn’t access your trading platform to manage the current open positions, or moreover, not being able to enter new trading opportunities because our systems are down. This can make a big difference in the year-end account review.
This is one of the most overlooked areas of algorithmic trading; it’s like an insurance premium…you hate paying it until the one time you ever need it saves you from a disaster.
Best Practices in Algorithmic Trading
Risk Management Strategies
Implementing effective risk management strategies in algorithmic trading is crucial to protect your investment and minimize losses.
One common approach is to set stop-loss orders, which automatically trigger the exit from a trade if its price reaches a predetermined level, for example. This helps limit potential losses and prevent emotional decision-making when market conditions are volatile.
Another risk management strategy is diversification. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, markets, and trading system correlations, you can reduce the impact of losses in one area. This ensures that your portfolio is not overly exposed to the performance of a particular security or sector.
Also, my favourite one is incorporating position sizing techniques, which can help manage risk.
You can control the potential downside by determining the appropriate allocation of capital for each trade based on factors such as risk tolerance, volatility and market conditions.
Risk management strategies protect your capital and add discipline to your trading approach.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Algorithmic trading is a dynamic field that requires continuous learning and adaptation. The more you acquire knowledge and experience, the more your way of trading changes and evolves, and the quicker you will become to adapt to market trends, strategies and technological changes.
Engaging in continuous learning involves reading books, attending workshops and webinars, participating in online forums and engaging with other members of the tradewithcode community to expand your knowledge. Understanding different trading theories, analysis tools, and market indicators and how to refine your trading strategies and make more informed decisions are fundamental skills that serious traders need to have.
Embracing a mindset of continuous learning and adaptation ensures that you stay ahead of the curve in algorithmic trading and maximize your potential for profitability.
[join the community]
Monitoring and Evaluation Techniques
To achieve success in algorithmic trading, it’s important to monitor and evaluate the performance of your trading strategies regularly. This allows you to identify any shortcomings or areas for improvement.
One way to monitor your strategies is through backtesting, which involves simulating your trading algorithms using historical data to assess their effectiveness. Backtesting helps determine if your strategies have a positive edge and if they can generate consistent profits over time.
Real-time monitoring is also crucial. By tracking the performance of your algorithms in live trading, you can identify any issues or anomalies that require immediate attention. This includes monitoring important factors such as order fill rates and slippage.
Remember, success in algorithmic trading is a continuous process of monitoring, evaluating, and making necessary adjustments to achieve optimal results.
Now that we’ve covered best practices in algorithmic trading let’s delve into another important aspect – developing effective trading strategies.
Common Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Algorithmic trading has revolutionized the way we approach the financial markets.
Advancements in technology and automated processes have opened up opportunities for traders to maximise profits and minimise risks.
In this section, I’d like to introduce three of the most common algorithmic trading strategies: Trend Following, Mean Reversion, and Arbitrage.
Trend Following
Trend following is a popular strategy in algorithmic trading that aims to capture profits by identifying and riding trends in the market.
The basic concept behind trend following is that once a trend is established, it is likely to continue in the same direction. Trading algorithms implementing this strategy will enter into long positions when the market is trending upwards and short positions when the market is trending downwards.
One effective tool in trend following is to use momentum indicators to identify trends as moving averages. For example, a 200-period moving average on a daily chart indicates where the trend is heading, even if the trend is lateral.
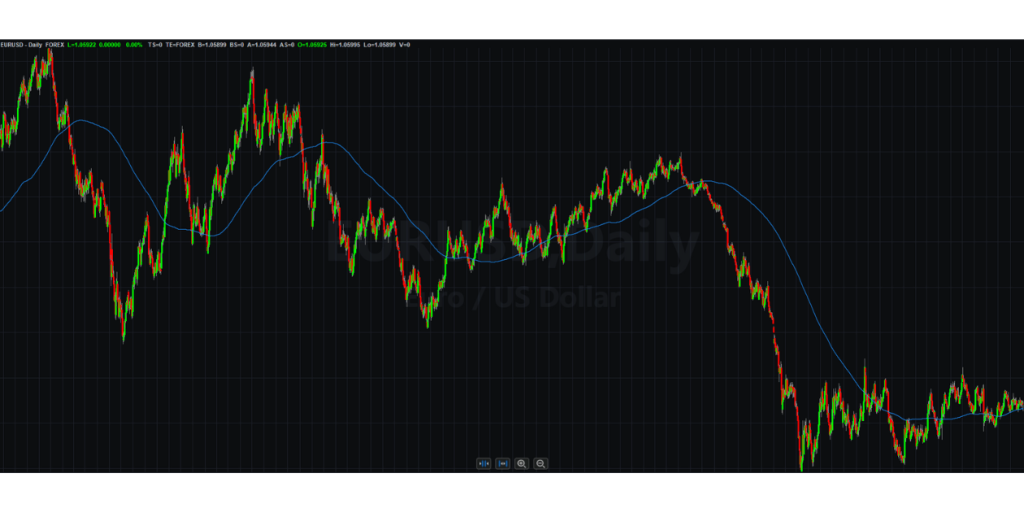
By following trends, trading algorithms can potentially enter trades to profit from the momentum of the market.
Mean Reversion
The mean reversion strategy is based on the concept that prices tend to move back to their average or mean over time.
Algorithms implementing this strategy evaluate the prices when they deviate too far from their average, entering into positions with the expectation that prices will revert to their mean, allowing traders to profit from the price correction.
This strategy often involves monitoring the price movements of specific assets and identifying instances where the price has deviated significantly from its average.
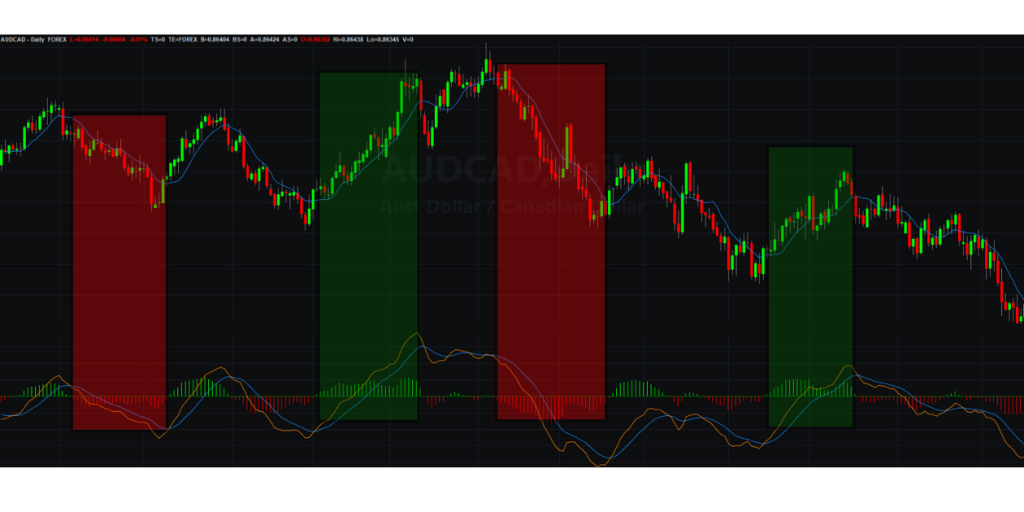
Usually, indicators that are in the oscillator category are used to detect the price divergence. The RSI and the MACD are the most common indicators in this category.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage is a strategy utilized by algorithmic traders to take advantage of price discrepancies across different markets or exchanges.
Algorithmic trading strategies simultaneously buy and sell assets in the same market (inter-market) or in different markets (intra-market) to profit from the price differences. This strategy requires quick execution and advanced algorithms to identify and exploit arbitrage opportunities.
Arbitrage opportunities can arise due to various factors, such as differences in supply and demand, exchange rate fluctuations, or inefficiencies in market pricing. By capitalizing on these price differences, traders can generate profits, spreading the risk across the entire arbitrage trade.
For example, we can automatically run arbitrage strategies on two different expirations of the same commodity future, such as crude oil (CL), and benefit from the price difference as I would sell the closest expiration contract and buy the in-the-future expiration contract.
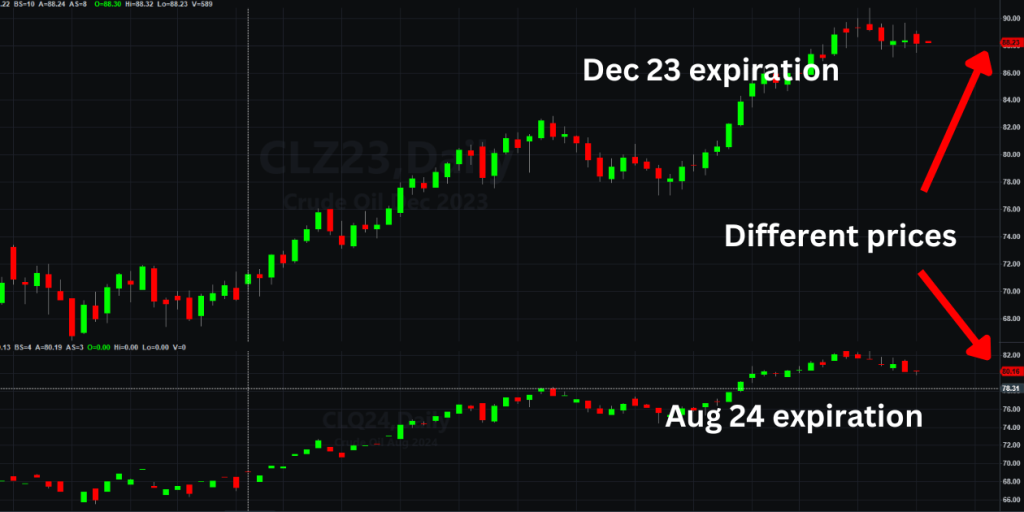
Implementing these algorithmic trading strategies requires a solid understanding of the market dynamics, robust technical analysis tools, and efficient execution systems.
Tools and Resources for Algorithmic Trading
Having the right tools and resources at your disposal is essential for being successful with algorithmic trading.
In this section, I want to share some of the key elements you need to consider when it comes to algorithmic trading software, data providers and APIs, as well as online communities and forums.
Algorithmic Trading Software
When it comes to algorithmic trading, the software you use plays a crucial role in executing your trading strategies effectively. Numerous algorithmic trading software options are available in the market, each with unique features and capabilities.
A popular software is TradeStation, the creators of EasyLanguage, which provides a user-friendly programming language that includes a wide range of built-in technical indicators, strategies and charting tools. There are many advantages to choosing TradeStation as the trading platform is directly connected with their brokerage services, offering platform and trading accounts an all-in-one solution. The disadvantage is that they don’t support trading the Forex market anymore.
Another notable option is MultiCharts, which offers an EasyLanguage platform compatible with their own implementation called PowerLanguage – I’d say that 80% of the strategies you run on TradeStation can run on MultiCharts. The model of this platform is that you purchase a licence of it, and you can connect almost any broker of your choice. I use Interactive Brokers and connected with the MultiCharts platform. If you are into cryptos, the crypto broker Binance is an option to do that. The list of supported brokers is long.
The disadvantage is that you need to have a data provider and pay for it, a different broker and connect all of them together using the MultiCharts platform. It’s a less straightforward setup compared to TradeStation, for sure.
Data Providers and APIs
Access to high-quality and reliable data is paramount to making informed trading decisions. Data providers offer a wide array of financial data, including historical price, fundamental, and news sentiment data.
One prominent data provider is Bloomberg, which is very expensive and very well-known for its comprehensive financial data offerings.
Other data feed providers, iQFeed and TradeStation offer the same data feeds used in the TradeStation platform through their own APIs for accessing real-time and historical market data.
Conclusion
Let’s conclude with a bold statement.
Algorithmic trading is a fascinating and powerful tool that can greatly enhance the trading experience for beginners.
By leveraging advanced logic models and automated systems, algorithmic trading allows for faster, more accurate decision-making and execution of trades. It reduces emotional biases and human errors that often are the reason for many mistakes in manual trading.
I can stress this enough, and I will be repeating myself: successful algorithmic trading requires continuous learning, testing, and optimization. It is a dynamic and evolving field, and staying up-to-date with the latest trends and techniques is essential.
Please let me know what you would like me to cover in more detail from this beginner’s guide in the comment, and I wish you happy trading!


